6.14 図形の面積
定理 6.52 (図形の面積)
曲線 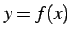 ,
, 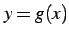 と直線
と直線 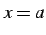 ,
, 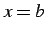 とで囲まれてできる領域の
面積は
とで囲まれてできる領域の
面積は
により求まる.
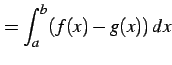 |
(1082) |
により求まる.
例 6.53 (図形の面積の計算例)
単位円 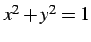 の内部の領域の面積を求める.
円の方程式は書き直すと
の内部の領域の面積を求める.
円の方程式は書き直すと
と表される.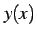 は 2 価関数である.
枝をそれぞれ
は 2 価関数である.
枝をそれぞれ
とおく.このとき円の面積は
と求まる.
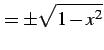 |
(1083) |
と表される.
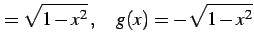 |
(1084) |
とおく.このとき円の面積は
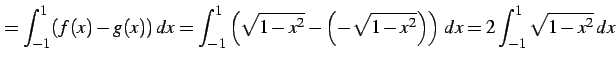 |
(1085) | |
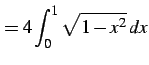 |
(1086) | |
| ( |
(1087) | |
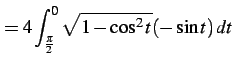 |
(1088) | |
| (積分区間をひっくり返す.
|
(1089) | |
 |
(1090) | |
| (
|
(1091) | |
 |
(1092) | |
| (
|
(1093) | |
![$\displaystyle = 2\int_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}(1-\cos 2t)\,dt= \Big[2t-\sin 2t\Big]_{0}^{\frac{\pi}{2}}= 2\times\frac{\pi}{2}-0-\sin(\pi)+\sin(0)=\pi$](img2093.png) |
(1094) |
と求まる.
Kondo Koichi

平成17年8月31日